 |
 |
 |
 |
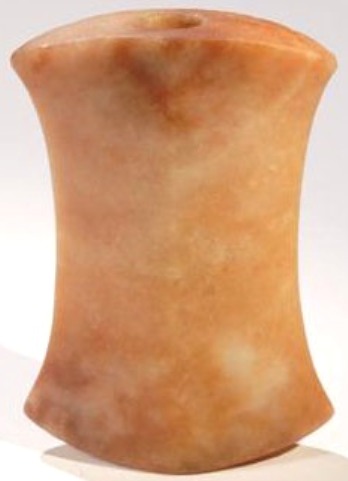
Ferruginous Quartz
Ferruginous quartz, sometimes called Hematoide, is a variety colored in yellow, red, or brown variations of differing intensities by inclusions of iron compounds, usually iron oxides and hydrous iron oxides, and hematite or limonite. These quartz crystals may comprise more than one color and are usually translucent or opaque.
The hydrous iron oxides in these crystals form and precipitate from watery solutions at relatively low temperatures, whereas hematite can also form in high temperature environments. Thus, ferruginous quartz can often be found in sedimentary rocks in and near hydrothermal veins and in iron ore deposits in the weathering zone near the surface that has been altered by oxidizing surface waters.
In the United States deposits with ferruginous quartz have been found in Middlesex County, Connecticut, the iron range of Michigan’s Upper Peninsula, Deer Lodge County, Montana, Rockingham County, New Hampshire, Lehigh County, Pennsylvania and Iron County, Utah.
Reference note by p4A editorial staff, November 2011.
